
Some things are just hard to look at like these disgusting tongues. They’re certainly not pretty, but they’re worth a look all the same. Just remember that some of them might be disturbing to some people, so viewer discretion is advised. With that in mind, let’s take a look at some of the most disturbing and disgusting tongues ever taken.
There’s something about tongues that just makes them gross.
Maybe it’s their slimy texture or the way they flap around when we speak. Whatever it is, tongue facts are enough to make anyone queasy. But if you’re curious (or just morbidly fascinated), read on for 25 disgusting facts about tongues! You might never look at yours the same way again…
NOTE: As promised, here are the photos that some people may find disturbing. I’m including this warning because I don’t want anyone to be caught off guard or upset after looking at them. With that said, please be aware that these images document real-life events, and they should not be viewed lightly. Thanks for understanding.
More reading:
- Why Does My Tongue Look Gross
- WATCH: 2-Minute Video Of Tongue Scraping…
- Baby Born With Enormous Tongue
- How to Pay Less for Medical Expenses
- Study: Pregnant Women With Medical Conditions More At Risk Than Older Pregnant Women

How Healthy is your Tongue?
Did you know that your tongue can give you some clues about your overall health? That’s right – by taking a close look at your tongue, you can get an idea of how healthy you are. The tongue is covered in tiny bumps called papillae, which contain taste buds. These taste buds allow us to experience different flavours, but they also help us to keep our tongues healthy.
When we eat and drink, the papillae trap bacteria and other particles. If these particles are not removed, they can build up and cause problems. That’s why it’s important to keep your tongue clean – brushing and scraping it regularly will help to remove any buildup and keep your tongue healthy.
So next time you take a look in the mirror, take a close look at your tongue – it just might be telling you something!
Power of your Tongue
Your tongue is covered in tiny bumps called papillae. These papillae help you to taste and also give your tongue its rough texture. Underneath the papillae, you have taste buds. Your taste buds are what allow you to taste things like sweet, sour, salty, and bitter.
You have between 2,000 and 4,000 taste buds on your tongue! Your tongue is also important for helping you to speak clearly. The muscles in your tongue help you to make different sounds when you talk.
Your tongue is also covered in mucus. This mucus helps to keep your mouth moist and also traps particles of food so that you can swallow them easily. Your tongue is a very important part of your mouth!
Do they look like disgusting tongues?
At first glance, your tongue may not look like the most appealing body part. It’s covered in grooves and bumps, and it’s often stained with food or bacteria. However, your tongue is actually a very important part of your body, and taking care of it is crucial for maintaining your oral health.
The papillae help you to keep food from getting stuck in your teeth. The grooves help to keep your taste buds moist so that they can function properly. And the bacteria on your tongue play an important role in breaking down food particles. So while your tongue may not be the prettiest body part, it’s still essential for keeping you healthy.
1. Severe Case of ‘Black Hairy Tongue’ Syndrome
The very creatively named ‘Black Hairy Tongue‘ looks awful, but it is only a temporary and harmless condition caused by a build-up of dead skin cells on the tongue. It can be caused by drinking too much coffee or ingesting lots of pureed foods.
Luckily, with a bit of tongue scraping and a better diet, Black Hairy Tongue syndrome won’t last more than a week or two.

Symptoms of Black Hairy Tongue
Discolouration
One of the most common signs of a black hairy tongue is a discolouration of the tongue. The tongue may appear to be black, brown, or even green. This is caused by a build-up of bacteria and debris on the surface of the tongue.
Hairy appearance
Another common sign of a black hairy tongue is a hairy appearance. The tongue may appear to be covered in hair-like projections. These projections are actually enlarged papillae, which are small bumps on the surface of the tongue.
Bad breath
Bad breath is another common sign of a black hairy tongue. This is due to the build-up of bacteria on the surface of the tongue. The bacteria can produce sulphur compounds, which can cause bad breath.
Causes of black hairy tongue
Poor oral hygiene
One of the most common causes of the black hairy tongue is poor oral hygiene. If you don’t brush and floss your teeth regularly, bacteria can build up on your tongue and cause it to become black and hairy.
Smoking
Smoking is another common cause of black hairy tongue. The nicotine and other chemicals in tobacco can discolour your tongue and make it more susceptible to bacterial growth.
Certain medications
Certain medications, such as antibiotics and antifungal drugs, can also cause a black hairy tongue. These drugs can kill the healthy bacteria in your mouth, which can lead to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria on your tongue.
2. Oral Thrush
Oral Thrush, also known as Oral Candidiasis, is a type of yeast infection that affects the mouth and throat. The yeast that causes oral thrush is a normal part of the flora of the mouth, but it can overgrow when the conditions are favourable. This can happen when there is a change in the pH of the mouth or a decrease in saliva production.
Oral thrush can also occur after taking certain antibiotics or steroids. Symptoms of oral thrush include white patches on the tongue and inside of the cheeks, redness and soreness in the mouth, and difficulty swallowing. Oral thrush is usually treated with antifungal medications, but it can recur.
To prevent oral thrush, good oral hygiene is essential. This includes brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and using a tongue scraper. Avoiding sugary foods and drinks can also help to prevent oral thrush.

Symptoms of Oral Thrush
White Patches on the Tongue
One of the most common symptoms of oral thrush is the presence of white patches on the tongue and inside of the cheeks. These patches may be painful, and they can make it difficult to eat or drink. The patches are caused by an overgrowth of a type of yeast called candida.
Redness and inflammation
Another common symptom of oral thrush is redness and inflammation in the mouth. This can cause a burning sensation in the mouth, and it may make it difficult to swallow. The redness and inflammation are caused by the candida yeast irritating the lining of the mouth.
Loss of taste
Oral thrush can also cause a loss of taste or a change in taste buds. This can make food taste different or bland. The loss of taste is caused by the candida yeast affecting the nerves that control taste.
Other symptoms include:
- Difficulty swallowing
- Pain when eating or drinking
- Cracks at the corners of the mouth
Causes of Oral Thrush
Poor Oral Hygiene
One of the most common causes of oral thrush is poor oral hygiene. If you don’t brush and floss your teeth regularly, food and bacteria can build up on your teeth and gums, which can lead to an overgrowth of yeast.
Use of antibiotics
Another common cause of oral thrush is the use of antibiotics – killing the good bacteria. Antibiotics kill both good and bad bacteria in the body, which can lead to an overgrowth of yeast.
Immune system disorders
Oral thrush can also be caused by immune system disorders, such as HIV/AIDS or diabetes. These disorders can weaken the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infection.
3. Green Smokers Tongue
Ever wonder why your tongue is green? No, it’s not because you’ve been licking too many lollipops! In most cases, a green tongue is harmless and simply a result of bacteria build-up – especially, from smoking. When bacteria collect on the tongue, it can cause the tongue to change colour.
This usually happens when people don’t brush their teeth regularly or clean their tongues properly. In addition, certain medications, such as antibiotics, can also cause the tongue to turn green.
While a green tongue is usually nothing to worry about, it can sometimes be a sign of an underlying medical condition. If you’re concerned about your green tongue, be sure to talk to your doctor.

Symptoms of Green Smokers Tongue
Discolouration
One of the most common symptoms of the green tongue is discolouration of the tongue. The tongue may appear to be green, yellow, or brown in colour. This discolouration is usually the result of bacteria or particles that have become trapped on the tongue.
Swelling
Another symptom of the green tongue is swelling. The tongue may appear to be larger than normal and may feel tender to the touch. This swelling is often the result of inflammation and can be painful.
Bad breath
Bad breath is another common symptom of the green tongue. This is usually caused by the bacteria that are present on the tongue. The bad breath may also be due to the particles that are trapped in the tongue like nicotine or cigarette particles.
Causes of Green Smokers Tongue
Poor oral hygiene
If you don’t brush and floss your teeth regularly, bacteria can build up on your tongue and cause it to turn green.
Smoking and illicit drug abuse
Smoking tobacco can also cause your tongue to turn green. This is because the tar and nicotine in cigarettes stain the tongue. Drugs can also affect the color of the tongue.
Underlying medical conditions
A green smokers tongue may be a symptom of various illnesses like leukoplakia, syphilis, oral thrush, and more.
4. Tongue Cancer
Cancer of the tongue can develop in any part of the tongue, but it most commonly affects the base of the tongue. The base of the tongue is the back third of the tongue, and it is anchored to the floor of the mouth. Cancer that develops in the base of the tongue is often difficult to detect in its early stages because it is hidden from view.
Tongue cancer is more likely to affect men than women, and it is most often diagnosed in people over the age of 50. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are major risk factors for developing tongue cancer. Symptoms of tongue cancer include a sore throat, trouble swallowing, and a lump on the tongue.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor for a diagnosis. Early detection is essential for the successful treatment of tongue cancer.

Symptoms of tongue cancer
A sore on the tongue that doesn’t heal
A sore on the tongue that doesn’t heal is a common symptom of tongue cancer. The sore may be red, white, or black and can bleed easily. It is important to see a doctor if you have a sore on your tongue that does not heal within two weeks.
Pain or numbness in the tongue
Pain or numbness in the tongue is another common symptom of tongue cancer. The pain may be constant or may only occur when eating or drinking. Numbness in the tongue can make it difficult to eat or drink and can also cause problems with speaking.
Swelling of the tongue
Swelling of the tongue is another symptom of tongue cancer. The swelling may make it difficult to breathe or swallow and can also cause the tongue to feel larger than normal. If you experience any swelling in your tongue, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible
Other symptoms include:
- red or white patches on the tongue
- lump on the tongue
- lump in the neck
- bleeding
Causes of tongue cancer
Smoking
One of the most common risk factors for tongue cancer is smoking. Tobacco use, including smoking cigarettes, cigars, and pipes, can damage the DNA in cells and lead to the development of cancer. People who smoke are also more likely to develop other forms of cancer, such as lung cancer and throat cancer.
Alcohol use
Another common risk factor for tongue cancer is alcohol use. Alcohol can damage the DNA in cells and lead to the development of cancer. People who drink alcohol are also more likely to develop other forms of cancer, such as liver cancer and throat cancer.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection
Another risk factor for tongue cancer is infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a sexually transmitted virus that can cause changes in the DNA of cells, which can lead to the development of cancer. People who are infected with HPV are also more likely to develop other forms of cancer, such as cervical cancer and throat cancer.
5. Fissured Tongue
A fissured tongue is a condition where the surface of the tongue appears to have deep grooves or cracks. It’s also sometimes called a cracked tongue, a grooved tongue, or a scrotal tongue. Although it can affect anyone, the fissured tongue is more common in older adults.
It’s also more likely to occur in people who have certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, psoriasis, and Sjogren’s syndrome. Fissured tongue isn’t harmful and doesn’t require treatment. However, some people may feel self-conscious about the way their tongue looks.
If you’re concerned about the appearance of your tongue, talk to your doctor or dentist. They can usually diagnose fissured tongue by looking at your mouth and tongue. In some cases, they may recommend a biopsy to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.

Symptoms of fissured tongue
Cracks or grooves on the surface of the tongue. While the fissured tongue is usually harmless, it can sometimes cause pain or discomfort when eating or talking. Additionally, the cracks on the surface of the tongue can trap food particles and bacteria, which can lead to bad breath. Treatment for the fissured tongue is typically not necessary, but some people may see a doctor to alleviate symptoms.
Causes of fissured tongue
While the exact cause of fissured tongue is unknown, it is believed to be genetic in nature. Additionally, the condition is often seen in people with other medical conditions, such as psoriasis or celiac disease.
6. White Coated Tongue
A white-coated tongue is a condition that can be caused by a build-up of bacteria, food debris, or dead cells on the surface of the tongue. This can give the tongue a white, coated appearance. While a white-coated tongue is usually nothing to worry about, it can sometimes be a sign of an underlying medical condition.
For example, if the coating is thicker than usual or if it is accompanied by other symptoms, such as bad breath or a sore throat, it could be a sign of oral thrush. Oral thrush is a fungal infection that affects the lining of the mouth and tongue.
If left untreated, it can spread to other parts of the body. If you are concerned about your symptoms, see your doctor for an evaluation.
Symptoms of white-coated tongue
While a white-coated tongue is usually harmless, it can sometimes be a sign of an underlying medical condition. The most common symptom of a white-coated tongue is, as the name suggests, a white film on the tongue. This film can vary in thickness and may cause the tongue to appear white or pale. Other symptoms of a white-coated tongue include bad breath, dry mouth, and a burning sensation on the tongue. In some cases, a white-coated tongue can also lead to difficulty swallowing or eating.
If you have any of these symptoms, it’s important to see your doctor or dentist so they can rule out any underlying medical conditions. The white-coated tongue is usually harmless, but in rare cases, it can be a sign of something more serious.

Causes of white-coated tongue
Poor oral hygiene
One of the most common causes of a white-coated tongue is poor oral hygiene. If you don’t brush and floss your teeth regularly, food and bacteria can build up on your tongue, causing it to become coated.
Dehydration
Dehydration can also cause your tongue to become coated. When your body is dehydrated, it doesn’t produce enough saliva to keep your mouth moist. This can lead to a buildup of bacteria on your tongue.
Dry mouth
A dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, is another common cause of a white-coated tongue. A dry mouth can be caused by a number of things, including medications, medical conditions, and mouth breathers.
Medical conditions
A white-coated tongue can be a sign of various medical conditions, including oral thrush, geographic tongue, leukoplakia, oral lichen planus, mouth cancer, tongue cancer, and syphilis. Oral thrush, for example, is a common infection in infants and toddlers that can cause white patches on the tongue. Although it’s usually harmless, oral thrush can be uncomfortable and difficult to treat.
Other medical conditions that can cause a white-coated tongue include geographic tongue (a condition that causes patches of the tongue to change colour), leukoplakia (a precancerous condition), oral lichen planus (an inflammatory condition), and mouth cancer or tongue cancer (both of which are rare but serious).
Lastly, syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection that can also cause a white-coated tongue. If you have any concerns about your white-coated tongue, be sure to talk to your doctor or dentist.
7. Geographic Tongue
Geographic tongue is a condition that results in patches on the tongue that are missing papillae. The tongue appears to have a map-like appearance. Geographic tongue is not contagious and is not dangerous. The condition is more genetically-linked.
It is not clear what causes geographic tongue, but it is thought to be linked to inflammation, nutritional deficiencies, or an autoimmune reaction. There is no cure for the geographic tongue, but the symptoms can be managed with topical treatments and oral hygiene measures.
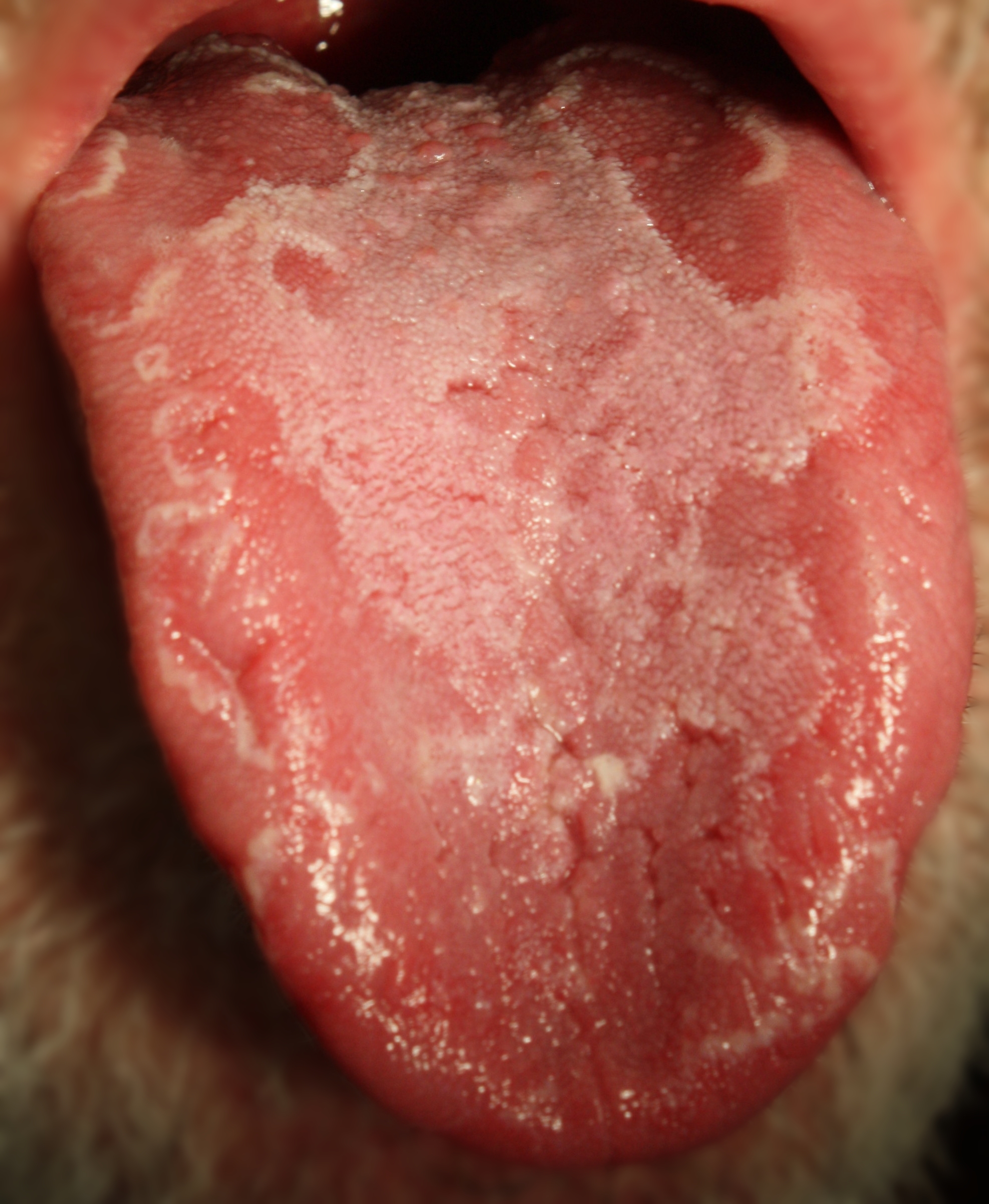
Symptoms of Geographic Tongue
- The patches can vary in size and shape, and they often have a scalloped or jagged border.
- The geographic tongue is usually painless, but some people may experience a burning sensation.
Causes of Geographic Tongue
Geographic tongue is a condition that can cause the tongue to develop patches of varying colours and textures. While the exact cause of geographic tongue is unknown, it is believed to be hereditary.
8. Strawberry Tongue
A strawberry tongue is a condition that causes the tongue to swell and develop a reddish, bumpy appearance. It is most often seen in children, but can also affect adults. The condition is usually harmless and will resolve on its own within a few days.
However, in some cases, the strawberry tongue can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as strep throat or scarlet fever. If the tongue does not improve within a few days, or if it is accompanied by other symptoms, such as fever or sore throat, it is important to see a doctor. With proper treatment, a strawberry tongue is usually not a serious condition.

Symptoms of Strawberry Tongue
White patches on the tongue
One of the most common symptoms of the strawberry tongue is the presence of white patches on the tongue. These patches can be either raised or flat and may have a slightly furry appearance. The patches may also be sore or itchy.
Swollen taste buds
Another symptom of the strawberry tongue is swollen taste buds. The taste buds may appear enlarged and may be more visible than usual. They may also be red or white in colour.
Burning sensation
Some people with strawberry tongues may also experience a burning sensation on their tongues. This sensation may be mild or severe and can make eating and drinking difficult.
Causes of Strawberry Tongue
Allergies
One of the most common causes of the strawberry tongue is allergies. Allergies can cause the tongue to swell and become inflamed, which can lead to the appearance of red bumps on the surface of the tongue. Allergies can be caused by a variety of things, including certain foods, pollen, and pet dander.
Infections
Infections are another common cause of strawberry tongue. Infections can cause the tongue to become red and swollen, and can also lead to the formation of red bumps on the surface of the tongue. Infections can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
Immune Disorders
Immune disorders such as autoimmune diseases can also cause strawberry tongue. Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system attacks healthy tissue, mistaking it for foreign invaders. This can lead to inflammation and swelling of the tongue, as well as the formation of red bumps on the surface of the tongue.
9. Chlamydia
Did you know that your tongue can reveal a lot about your health? For example, a swollen and discoloured tongue can indicate anemia, while white spots may indicate a fungal infection. And if your tongue is coated with a thick, white film, it could be a sign of an underlying medical condition known as chlamydia.
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection that affects the mucous membranes of the genitals and rectum. It’s caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis and is often passed from one person to another through sexual contact. Symptoms of chlamydia include burning during urination, discharge from the penis or vagina, and pain in the testicles or ovaries.
In some cases, chlamydia can also cause inflammation of the Bartholin’s glands, which are located near the vaginal opening. If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to serious health problems such as pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility, and ectopic pregnancy.
If you think you may have chlamydia, it’s essential to see a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment. Fortunately, chlamydia is easy to treat with antibiotics. However, finishing all the medication your healthcare provider prescribes is necessary, even if your symptoms go away. Otherwise, the infection could come back and cause more severe health problems.

Symptoms of Chlamydia on the tongue
Sores or lesions in the mouth
One of the most common symptoms of an oral STD is the presence of sores or lesions in the mouth. These sores can be painful and may make it difficult to eat or drink. They can also be unsightly and may cause embarrassment.
Swollen lymph nodes
Another symptom of an oral STD is swollen lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped glands that are found throughout the body. They help to filter out bacteria and other toxins from the body. When they become swollen, it is usually a sign that something is wrong.
Fever
Fever is another symptom that may be associated with an oral STD. A fever can be a sign of infection and should always be taken seriously. If you have a fever, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible so that you can get treatment.
Causes of chlamydia
- Chlamydia is caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis.
- Chlamydia is usually transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
- Chlamydia can also be transmitted from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth.
- People who have multiple sexual partners or who do not use condoms during sex are at a higher risk of contracting chlamydia.
- People with a weakened immune system are also at a higher risk of contracting chlamydia.
10. Syphillis
One such condition is syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection that can cause a range of symptoms, including tongue lesions. Syphilis is caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum, and it can be passed from person to person through sexual contact. The disease progresses through three stages: primary, secondary, and tertiary. In the primary stage, a small sore called a chancre develops at the site of infection.
The chancre is usually painless, but it can sometimes be accompanied by swollen lymph nodes. The secondary stage is characterized by a rash that typically appears on the palms of the hands or the soles of the feet. The rash is often accompanied by flu-like symptoms, such as fever and fatigue.
In the tertiary stage, syphilis can damage the brain, heart, and other organs. Tongue lesions are one of the most common manifestations of tertiary syphilis, and they can cause the tongue to take on a yellowish-brown colour. If left untreated, syphilis can be fatal.

Symptoms of syphilis on the tongue
White spots
One of the most common symptoms of syphilis on the tongue is the presence of white spots. These spots are typically small and painless, but can sometimes be large and painful. They are often mistaken for canker sores or other mouth infections.
Sores
Syphilis can also cause sores on the tongue. These sores are typically red or white and can be either painless or painful. They may also bleed easily.
Swelling
Another symptom of syphilis on the tongue is swelling. The tongue may become swollen and enlarged, making it difficult to speak or eat. In severe cases, the tongue may become so swollen that it blocks the airway, which can be life-threatening.
Causes of syphilis
- The bacteria that cause syphilis are passed from person to person through sexual contact.
- You can get syphilis by having unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has the infection.
- Syphilis can also be passed from an infected mother to her unborn child during pregnancy or delivery.
11. Canker Sores
Canker sores are small, shallow ulcers that develop on the soft tissues in your mouth, such as your gums, tongue, inner cheeks, and lips. They’re usually white or yellow with a red border and can be extremely painful. Canker sores are not contagious, but they can reoccur.
There are several possible causes of canker sores, including physical trauma (such as biting your cheek), viral infections (such as the herpes simplex virus), autoimmune conditions (such as Crohn’s disease), nutritional deficiencies (such as a lack of vitamin B12), and stress.
There is no cure for canker sores, but there are several ways to manage the pain and speed up healing, such as using topical medications or taking over-the-counter pain relievers. If you have a canker sore that is large or persistent, you should see your doctor or dentist for treatment.

Causes of canker sores
There are several different causes of canker sores, including:
- A reaction to certain foods or chemicals
- A viral infection
- A bacterial infection
- An autoimmune reaction
- Stress
- Hormonal changes
12. HIV Mouth Sores
HIV mouth sores are a common symptom of the virus. They can appear as red, white, or purple spots on the gums, tongue, or inside of the cheeks. HIV mouth sores can also be painful and make it difficult to eat or drink. In some cases, they may also lead to weight loss.
The good news is that HIV mouth sores are treatable. With early diagnosis and treatment, most people with HIV can manage their symptoms and enjoy a long, healthy life. If you think you may have HIV mouth sores, it’s important to see a doctor as soon as possible for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.

Symptoms of HIV Mouth Sores
- HIV mouth sores are small, red, or white lesions that can develop in the mouth of someone who has HIV.
- HIV mouth sores are often painful and can make it difficult to eat or drink.
- HIV mouth sores can also cause fever, fatigue, and weight loss.
Causes of HIV mouth sores
Trauma to the mouth
One of the most common causes of mouth sores is trauma to the mouth, such as from tooth brushing or eating hard foods. This can cause the tissue in the mouth to become irritated and inflamed, leading to the development of sores.
STD infections
Mouth sores can also be caused by infections, such as viral infections like herpes simplex virus (HSV) or HIV. These infections can cause inflammation and irritation of the tissue in the mouth, leading to the development of sores.
Autoimmune disorders
Autoimmune disorders, such as Crohn’s disease or lupus, can also cause mouth sores. These disorders occur when the body’s immune system attacks healthy tissue, leading to inflammation and irritation.
13. Mild Oral Hairy Leukoplakia
Mild Oral Hairy Leukoplakia (MOHL) is a lesion that appears on the tongue. It is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, which is the same virus that causes mononucleosis. The lesion consists of white, hairy patches that may be slightly raised. MOHL is benign and does not cause any pain or discomfort.
However, it can sometimes be mistaken for oral thrush or leukoplakia, which are both more serious conditions. MOHL is typically diagnosed by a biopsy, which is a simple procedure that involves removing a small sample of tissue from the lesion. Treatment is not usually necessary, as the lesion will typically resolve on its own within a few weeks. However, if the lesion does not go away or if it recurs, treatment with antiviral medication may be recommended.

Symptoms of MOHL
White patches on the tongue
One of the most common symptoms of oral hairy leukoplakia is the presence of white patches on the tongue. These patches can vary in size and may be raised or flat. They may also have a hairy or velvety appearance.
Burning sensation
Some people with oral hairy leukoplakia may also experience a burning sensation on their tongue. This sensation may be mild or severe and can make it difficult to eat or drink.
Swelling of the tongue
In some cases, oral hairy leukoplakia can cause the tongue to swell. This swelling can make it difficult to speak or swallow. In severe cases, it may even cause the tongue to block the airway, which can be life-threatening.
Causes of MOHL
Epstein-Barr Virus
One of the most common causes of mild oral hairy leukoplakia is the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). EBV is a virus that is responsible for causing mononucleosis, also known as “mono.” Mono is a viral infection that can cause fatigue, sore throat, and fever. While EBV is typically harmless, it can lead to oral hairy leukoplakia in people with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS.
Human Papillomavirus
Another common cause of mild oral hairy leukoplakia is the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a virus that can cause warts on the skin or mucous membranes. While HPV is typically harmless, it can lead to oral hairy leukoplakia in people with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS.
Oral Thrush
Oral thrush is another common cause of mild oral hairy leukoplakia. Oral thrush is a condition that occurs when the fungus Candida albicans grows out of control in the mouth. People with oral thrush may experience white patches on their tongue or inner cheeks, as well as redness and soreness. While oral thrush is usually not serious, it can lead to oral hairy leukoplakia in people with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS
14. Blue Tongue
Blue Tongue is a condition that can be caused by a lack of oxygen in the blood. It can also be caused by eczema, which is a condition that causes the skin to become inflamed. When the skin is inflamed, it can cause the blood vessels to constrict, which can lead to a lack of oxygen in the blood.
Blue Tongue can also be caused by an allergic reaction to certain foods or chemicals. In some cases, Blue Tongue can be caused by a virus or bacteria. If you think you may have Blue Tongue, it is important to see a doctor so that they can diagnose and treat the condition.

Symptoms of Blue Tongue
Blue tongue is a condition that can cause a blue or purple discolouration of the tongue. In some cases, discolouration may also involve the lips, gums, or inside of the cheeks. Although blue tongue is usually harmless, it can sometimes be a sign of a more serious condition.
Symptoms of blue tongue include a blue or purple tongue, as well as possible swelling of the tongue. In some cases, blue tongue may also cause difficulty breathing or swallowing. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis. Blue tongue is often caused by a lack of oxygen in the blood, but it can also be due to certain types of eczema or other skin conditions.
Treatment for blue tongue typically involves treating the underlying condition. In most cases, blue tongue will resolve on its own without any treatment. However, if the condition is caused by a more serious condition, such as eczema, treatment may be necessary to prevent complications.
Causes of Blue Tongue?
There are several potential causes of blue tongue in humans. One possibility is a lack of oxygen. This can happen if the person is not breathing properly, or if they have a medical condition that affects their ability to get oxygen to their tissues. Another possibility is eczema. This is a skin condition that can cause the skin to become irritated and inflamed, and it can sometimes lead to blue discolouration. F
inally, another potential cause of blue tongue is an infection. This could be a bacterial or viral infection, and it may cause the tongue to turn blue as a result of inflammation. If you are concerned about blue tongue, speak to your doctor for more information.
15. Kawasaki Disease or Bright Red Tongue
Kawasaki disease is a rare illness that primarily affects young children. It is characterized by a bright red tongue, fever, and lymph node swelling. In some cases, Kawasaki disease can also lead to heart problems. The exact cause of Kawasaki disease is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by an infection or immune reaction.
Treatment typically involves the use of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications. With proper treatment, most children make a full recovery from Kawasaki disease. However, some children may experience long-term heart problems as a result of the illness.

Symptoms of Kawasaki Disease
Fever
One of the most common symptoms of Kawasaki disease is a fever that lasts for more than five days. The fever may be as high as 104 degrees Fahrenheit and is often accompanied by a rash.
Irritability
Another symptom of Kawasaki disease is irritability. Children with Kawasaki disease may be unusually fussy or cranky and may have difficulty sleeping.
Swollen lymph nodes and tongue
Swollen lymph nodes are another common symptom of Kawasaki disease. The lymph nodes may be swollen in the neck, mouth, tongue, under the arms, or in the groin area.
Causes of Kawasaki Disease
- Kawasaki disease is a rare illness that primarily affects young children.
- The exact cause of Kawasaki disease is unknown, but it is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Some of the possible environmental factors that may contribute to the development of Kawasaki disease include exposure to certain viruses or bacteria or exposure to toxic chemicals.
16. Lichen Planus Tongue
Lichen planus is a condition that can affect the skin, nails, and mucous membranes. The most common symptom is a rash that appears as raised, flat bumps that are often itchy or painful. The bumps may be purple, red, or white, and they may be covered with small scales. In some cases, the bumps can blister or ulcerate.
Lichen planus can also cause changes in the nails, such as pitting, thinning, or lifting of the nail from the bed. In rare cases, lichen planus can affect the mucous membranes, causing lesions to form on the tongue or inside the mouth. Treatment for lichen planus typically involves topical corticosteroids or other anti-inflammatory medications. In severe cases, oral steroids may be necessary.
Most people with lichen planus eventually recover without any long-term problems. However, in some cases, the condition can become chronic.
Symptoms of Lichen Planus Tongue
- White or silver patches on the tongue
- Soreness or burning sensation on the tongue
- Swelling of the tongue
Causes of Lichen Planus Tongue
Lichen planus is a condition that can affect the skin, nails, and mucous membranes. The tongue is a common site for lichen planus lesions, which typically appear as white or silver patches. These patches may be accompanied by a sore or burning sensation. In some cases, the tongue may also swell.
Autoimmune disorder
Lichen planus is an autoimmune disorder. This means that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues. In the case of lichen planus, the immune system attacks the cells in the mucous membranes.
Allergies
Allergies are another possible cause of lichen planus. Allergies can trigger an immune response, which may cause the body to attack healthy tissue.
Medications
Certain medications can also cause lichen planus. These include beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and quinine. If you are taking any of these medications and develop symptoms of lichen planus, be sure to talk to your doctor.
17. Heart Disease
Heart disease is a general term used to describe a variety of conditions that affect the heart. Symptoms can vary depending on the type of heart disease, but they may include chest pain, shortness of breath, and an irregular heartbeat.
A redder tongue with a yellow coating can also be a symptom of heart disease. The tongue may appear red because of inflammation or poor circulation. The yellow coating is often the result of a build-up of plaque on the tongue. If you notice any changes in your tongue, it is important to see a doctor for an evaluation.
Heart disease is a serious condition that can lead to death if it is not treated. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for preventing complications from heart disease.

Symptoms of Heart Disease
Chest pain or discomfort
One of the most common symptoms of heart disease is chest pain or discomfort. This pain can feel like a squeezing sensation, and it may be accompanied by shortness of breath, nausea, or lightheadedness. If you experience any type of chest pain, it’s important to see a doctor as soon as possible, as it could be a sign of a heart attack.
Pain in the jaw, neck, or arms
Another common symptom of heart disease is a pain in the jaw, neck, or arms. This pain is often caused by decreased blood flow to the heart muscle. The pain may feel like a dull ache or a sharp shooting sensation. If you experience any type of jaw, neck, or arm pain, it’s important to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath is another common symptom of heart disease. This symptom can be caused by a variety of factors, including decreased blood flow to the heart muscle and fluid buildup in the lungs. If you experience shortness of breath, it’s important to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Causes of Heart Disease
Unhealthy diet
One of the primary causes of heart disease is an unhealthy diet. A diet that is high in saturated and trans fats, as well as refined carbohydrates, can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can eventually lead to heart disease. Additionally, a diet that is lacking in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can also increase the risk of heart disease.
Lack of exercise
Another cause of heart disease is a lack of exercise. Physical activity helps to keep the arteries clear and reduces the risk of plaque buildup. Additionally, exercise helps to lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, both of which are risk factors for heart disease.
Smoking
Smoking is another major cause of heart disease. Cigarette smoke contains a variety of harmful chemicals that damage the arteries and increase the risk of plaque buildup. Additionally, smoking increases blood pressure and decreases the amount of oxygen that reaches the heart.
18. Burning Mouth Syndrome
Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is a complex oral condition that is characterized by a burning sensation in the mouth. The burning may be constant or intermittent, and it can affect the tongue, gums, palate, or lips. BMS is often diagnosed in middle-aged women, although it can affect people of any age or gender.
The exact cause of BMS is unknown, but numerous factors have been linked to the condition, including psychological stress, nutritional deficiencies, menopause, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions. There is no cure for BMS, but treatments are available to help relieve symptoms.
These include oral sprays, lozenges, and antidepressants. In some cases, dietary changes may also be recommended. With proper treatment, most people with BMS are able to manage their symptoms and enjoy a good quality of life.

Symptoms of burning mouth syndrome
Burning sensation
One of the most common symptoms of burning mouth syndrome is a burning sensation in the mouth. This sensation can be constant or it can come and go. It may be worse in the morning or after eating. The burning sensation can be mild or severe.
Painful sensation
Another symptom of burning mouth syndrome is a painful sensation in the mouth. This pain may be constant or it may come and go. It may be worse in the morning or after eating. The pain can be mild or severe.
Sensitivity to heat and cold
People with burning mouth syndrome may also experience sensitivity to heat and cold. This means that hot and cold beverages may cause discomfort. Hot foods may also cause pain.
Cause of burning mouth syndrome
Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is a condition that causes burning pain in the mouth. The exact cause of BMS is unknown, but it is thought to be related to changes in the nervous system or changes in the levels of hormones or other chemicals in the body.
BMS can be caused by a variety of factors, including psychological stress, nutritional deficiencies, menopause, certain medications, and infections.
There are treatments that can help to relieve the symptoms. These include oral rinses, topical gels or creams, and antidepressants.
19. Smooth Tongue or Atrophic Glossitis
Smooth tongue, or atrophic glossitis, is a condition characterized by the loss of papillae, the small bumps on the surface of the tongue. This can lead to a smooth, shiny appearance. While it is not typically painful, it can cause some discomfort and make it difficult to taste food.
In some cases, it can also be linked to other conditions, such as anemia or vitamin deficiencies. Treatment usually involves addressing the underlying cause, if one can be identified. In some cases, however, the cause is unknown and treatment focuses on relieving symptoms.

Symptoms of Smooth Tongue or Atrophic Glossitis
- The tongue may appear red, smooth, and shiny.
- The tongue may have a loss of taste buds, which can lead to a decrease in the ability to taste sweet, sour, or salty flavours.
- The tongue may have difficulty moving and may feel stiff or thick.
Causes of Smooth Tongue or Atrophic Glossitis
Deficiency in vitamins and minerals
A deficiency in certain vitamins and minerals can lead to smooth tongue or atrophic glossitis. For example, a lack of vitamin B12 can lead to a condition called pernicious anemia, which can cause smooth tongue. A lack of iron can also lead to atrophic glossitis.
Autoimmune disorders
Autoimmune disorders occur when the body’s immune system attacks healthy tissue. autoimmune disorders that can lead to smooth tongue or atrophic glossitis include celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, and lupus.
Medications
Certain medications can also lead to smooth tongue or atrophic glossitis. For example, antacid medications that contain aluminum can cause a condition called oral lichen planus, which can lead to smooth tongue. Medications that contain isotretinoin, such as Accutane, can also lead to atrophic glossitis.
20. Macroglossia
Macroglossia is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal enlargement of the tongue! The tongue can grow to be two or three times its normal size, which can cause difficulties with speaking and eating. In severe cases, the tongue can block the airway, making it difficult to breathe. Macroglossia can be caused by a number of conditions, including diabetes, thyroid disease, and genetic disorders.
Treatment typically involves reducing the size of the tongue through surgery. In some cases, a portion of the tongue may need to be removed. In other cases, implants or devices may be used to hold the tongue in place. With treatment, most people with macroglossia are able to lead normal, healthy lives.

Symptoms of macroglossia
Enlarged tongue
One of the most obvious symptoms of macroglossia is an enlarged tongue. The tongue may appear to be significantly larger than normal, and it may protrude from the mouth more than usual. In some cases, the tongue may be so large that it interferes with breathing or speaking.
Difficulty swallowing
Another symptom of macroglossia is difficulty swallowing. The enlarged tongue can make it difficult to move food or liquid around in the mouth, and it may also make it more likely for food or liquid to be aspirated into the lungs. Aspiration can lead to pneumonia or other respiratory problems.
Sleep apnea
Sleep apnea is a condition in which a person stops breathing for brief periods during sleep. It can occur when the tongue is too large and blocks the airway. Sleep apnea can cause fatigue, daytime sleepiness, and other health problems.
Causes of macroglossia
Obesity
One of the most common causes of macroglossia is obesity. When a person is obese, they have excess body fat. This excess body fat can cause the tongue to enlarge, which can lead to macroglossia. Obesity is a major problem in many countries and is a leading cause of preventable death.
Diabetes
Diabetes is another common cause of macroglossia. Diabetes is a condition that occurs when there is too much sugar in the blood. This can happen if the body does not produce enough insulin, or if the body does not use insulin properly. Diabetes can cause damage to the nerves and blood vessels, which can lead to tongue enlargement.
Amyloidosis
Amyloidosis is a condition that occurs when there is an accumulation of amyloid proteins in the body. Amyloid proteins are abnormal proteins that can build up in various organs, including the tongue. Amyloidosis can cause the tongue to swell and become enlarged.
21. Diphtheria Tongue
Diphtheria is a potentially deadly bacterial infection that primarily affects the nose and throat. The bacteria secrete a toxin that can damage the tissues, leading to inflammation and the formation of a thick membrane. This membrane, known as a diphtheritic membrane, can block the airway and make it difficult to breathe. In some cases, the toxin can also affect the heart and nervous system, which can be fatal.
Diphtheria is most commonly spread through close contact with an infected individual, such as sharing cups or utensils. The best way to prevent the spread of diphtheria is to practice good hygiene and get vaccinated. Early diagnosis and treatment are also essential for preventing serious complications.
Diphtheria tongue is one of the most common symptoms of diphtheria infection. It refers to the thick, white membrane that forms on the tongue and can make it difficult to speak or swallow. Diphtheria tongue can also cause bad breath and a sore throat. If you think you may have diphtheria, it is important to see a doctor immediately so that you can receive treatment.

Symptoms of Diphtheria
White patches
One of the most common symptoms of diphtheria is the presence of white patches on the tongue. These patches are usually thick and can make it difficult to swallow or breathe. In some cases, the patches can also bleed.
Swollen glands
Another symptom of diphtheria is swollen glands. The glands may be swollen in the neck, armpits, or groin. This can cause pain and make it difficult to move the affected limb.
Fever
Fever is another common symptom of diphtheria. The fever may be accompanied by chills, sweats, and general feelings of fatigue. In some cases, the fever can be high enough to cause delirium or seizures
Causes of Diphtheria
Bacteria
Diphtheria is caused by a bacteria called Corynebacterium diphtheriae. This bacteria typically live in the nose and throat of humans and is spread through close contact with an infected person, such as coughing or sneezing. The bacteria produce a toxin that can damage the heart, nerves, and kidneys.
Poor hygiene
Diphtheria is more common in areas with poor hygiene conditions. This is because the bacteria that cause diphtheria thrive in crowded, unsanitary conditions. Close contact with an infected person is more likely in these conditions, which increases the spread of the bacteria.
Lack of vaccination
Diphtheria can also be prevented through vaccination. The diphtheria vaccine is typically given as part of a combination vaccine that also protects against tetanus and pertussis (whooping cough). The vaccine is most effective when given to children under the age of seven.
22. Tongue Herpes
Tongue herpes is a viral infection that causes sores or lesions on the tongue. The virus responsible for tongue herpes is the same one that causes cold sores, which is why the two conditions share many of the same symptoms. Tongue herpes is most commonly caused by the HSV-1 virus, although the HSV-2 virus can also be responsible for causing the condition.
Symptoms of tongue herpes include tingling or burning sensations on the tongue, as well as redness and swelling. The lesions caused by the virus can be painful and may make it difficult to eat or drink. In some cases, tongue herpes can also cause fever and swollen lymph nodes.
There is no cure for tongue herpes, but the symptoms can be treated with antiviral medications. In most cases, the virus will eventually go into remission on its own. However, the virus can be re-activated at any time, which is why it is important to practice good oral hygiene and avoid triggers such as stress or illness.
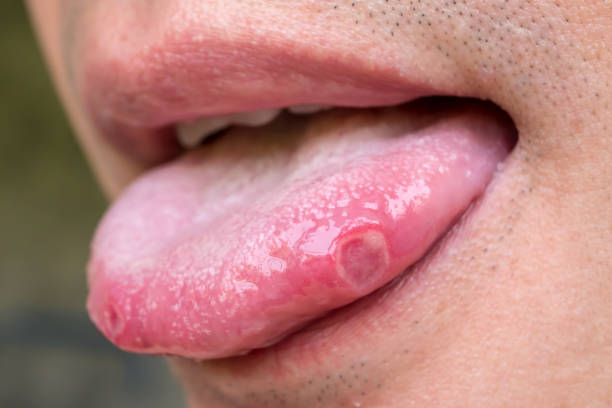
Symptoms of Tongue Herpes
Sores
One of the most common symptoms of tongue herpes is the presence of sores on the tongue. These sores can be painful and may make it difficult to eat or drink. The sores may also bleed.
Swelling
Another common symptom of tongue herpes is swelling of the tongue. This swelling can make it difficult to speak or eat. In severe cases, the tongue may swell so much that it blocks the airway and makes it difficult to breathe.
Burning sensation
A burning sensation on the tongue is another common symptom of tongue herpes. This burning sensation can be very painful and may make it difficult to eat or drink.
Causes of Tongue Herpes
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1)
HSV-1 is the most common cause of tongue herpes. This virus is typically spread through contact with saliva, such as kissing or sharing utensils with someone who has the virus. HSV-1 can also be spread through contact with infected bodily fluids, such as blood.
Herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2)
HSV-2 is the second most common cause of tongue herpes. This virus is typically spread through sexual contacts, such as oral, vaginal, or anal sex. HSV-2 can also be spread through contact with infected bodily fluids, such as blood.
Other viruses
There are a number of other viruses that can cause tongue herpes, including the Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and human papillomavirus. These viruses are typically spread through contact with saliva or infected bodily fluids.
23. Median Rhomboid Glossitis
Median rhomboid glossitis is a condition that results in inflammation of the tongue. The tongue is made up of many different types of tissue, including muscles, nerves, and blood vessels. The inflammation of median rhomboid glossitis typically affects the mucous membranes that line the tongue. Symptoms of median rhomboid glossitis include redness, swelling, and soreness.
According to the NCBI, median rhomboid glossitis affects the central papillary atrophy of the tongue.
The condition can also cause difficulty eating and talking. In some cases, median rhomboid glossitis can lead to an overgrowth of yeast or bacteria on the tongue, which can cause bad breath. Treatment for median rhomboid glossitis typically involves antifungal or antibiotic medications. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected tissue.
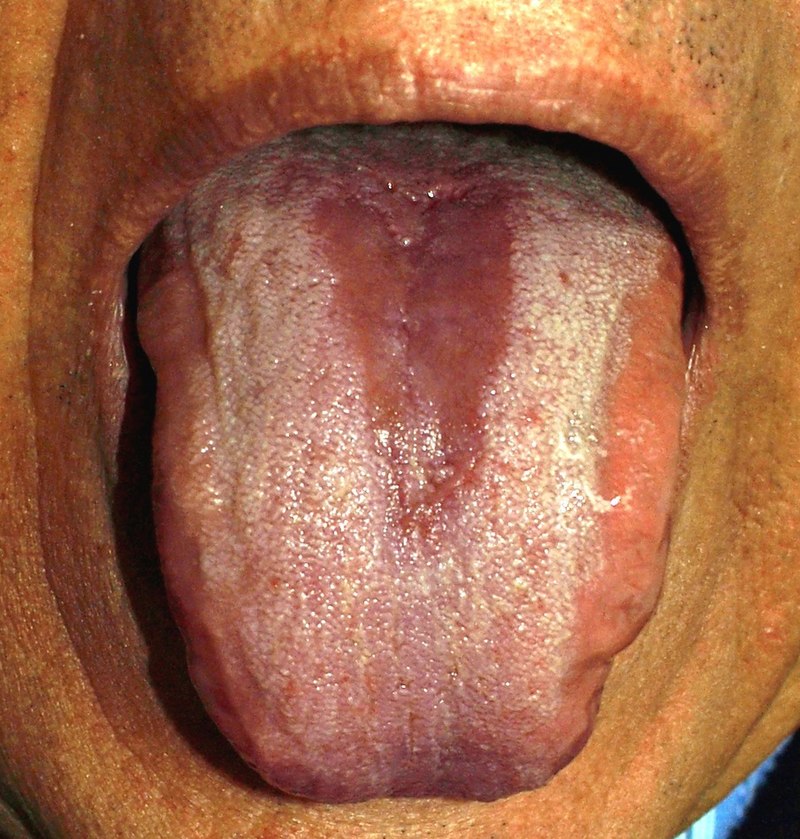
Symptoms of Median Rhomboid Glossitis
- Median Rhomboid Glossitis is a condition that affects the tongue, especially in the middle of the dorsum.
- The main symptom of median rhomboid glossitis is a red, raised area on the tongue that may be painful or itchy.
- Other symptoms of median rhomboid glossitis include a burning sensation on the tongue, soreness, and difficulty eating or swallowing.
Causes of Median Rhomboid Glossitis
- Median Rhomboid Glossitis is a condition that results in inflammation of the tongue.
- The exact cause of median rhomboid glossitis is unknown, but it is believed to be linked to an overgrowth of yeast in the mouth.
- Median Rhomboid Glossitis is more common in people who have certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or HIV/AIDS. It is also more common in people who smoke tobacco or use mouthwash that contains alcohol.
24. Ankyloglossia or Tongue-Tie
Ankyloglossia, or tongue-tie, is a condition that limits the mobility of the tongue. The tongue is attached to the floor of the mouth by a thin strip of tissue, called the frenulum. In people with ankyloglossia, the frenulum is abnormally short or tight, which restricts the movement of the tongue.
Ankyloglossia can cause problems with breastfeeding, speaking, and eating. It can also lead to oral hygiene issues, such as an increased risk of gum disease. Treatment for ankyloglossia typically involves surgically releasing the frenulum. This procedure is usually safe and effective, and it can provide significant relief from symptoms.

25. People who were born without a tongue!
Can you imagine not having a tongue? For some people, this is a reality! There are a few different reasons why someone may be born without a tongue. In some cases, it is due to a genetic mutation or abnormality. Other times, it may be the result of an injury or illness that affects the development of the tongue in the womb.
Regardless of the cause, living without a tongue can be challenging. Those who are born without a tongue often have difficulty eating and speaking. They may also experience dry mouth and other oral health problems. Despite these challenges, many people who are born without a tongue learn to adapt and lead full, rich lives.




 Top 14 Online Adult Shops in Australia
Top 14 Online Adult Shops in Australia  List of Environmentally Friendly Disposable Nappies (and...
List of Environmentally Friendly Disposable Nappies (and...  List of the Best Weight Loss Shake...
List of the Best Weight Loss Shake...  Where to Buy Wholesale Vibrators to Sell...
Where to Buy Wholesale Vibrators to Sell...  Our Honest Bed Threads Review 2021
Our Honest Bed Threads Review 2021 



